Credit cards are rectangular cards made of plastic or metal which are issued by a bank or a financial institution. These enable the card holder to pay from borrowed funds for purchase of goods and services to merchants who accept cards for payment. The card holder has to repay the borrowed money along with any interest and other charges as per the agreement on or before the due date.
In addition to the the credit, the issuing bank or financial institution may also provide cash advance withdrawal facility through ATM’s upto a certain amount. Such cash advances normally attract higher interest rates and charges compared to the usage of standard credit line.
Table of Contents
Features of a credit card
- Quick & Instant Approval – These days one can apply for a credit card online and receive instant approval. The credit card is generally couriered to the card holder within a few days.
- Credit Limit – Every credit card has a customized credit limit. The credit limit is determined basis the applicant’s income range, credit score and other criteria.
- Secured Transactions – Credit cards these days offer ‘Chip’ and ‘PIN’ security. One can also have WiFi enabled credit cards which enable contactless payment. These don’t have to be swiped. The card has to be tapped against the card reader to complete the transaction.
- EMI facility – Most of the credit cards today provide a facility to convert a large purchase amount into an EMI. One can pay the amount as ‘equated monthly installments’ (EMI) over a period of time. This feature is useful when a large amount has to be paid upfront like buying electronic gadgets, paying hospital bills, school fees etc. The credit card issuing bank may levy charges and interest as per bank policy.
- Cash Withdrawal – As mentioned earlier, many credit cards today also provide the facility to withdraw cash from ATM’s upto a certain limit. This feature is very useful when one is in need of emergency cash credit.
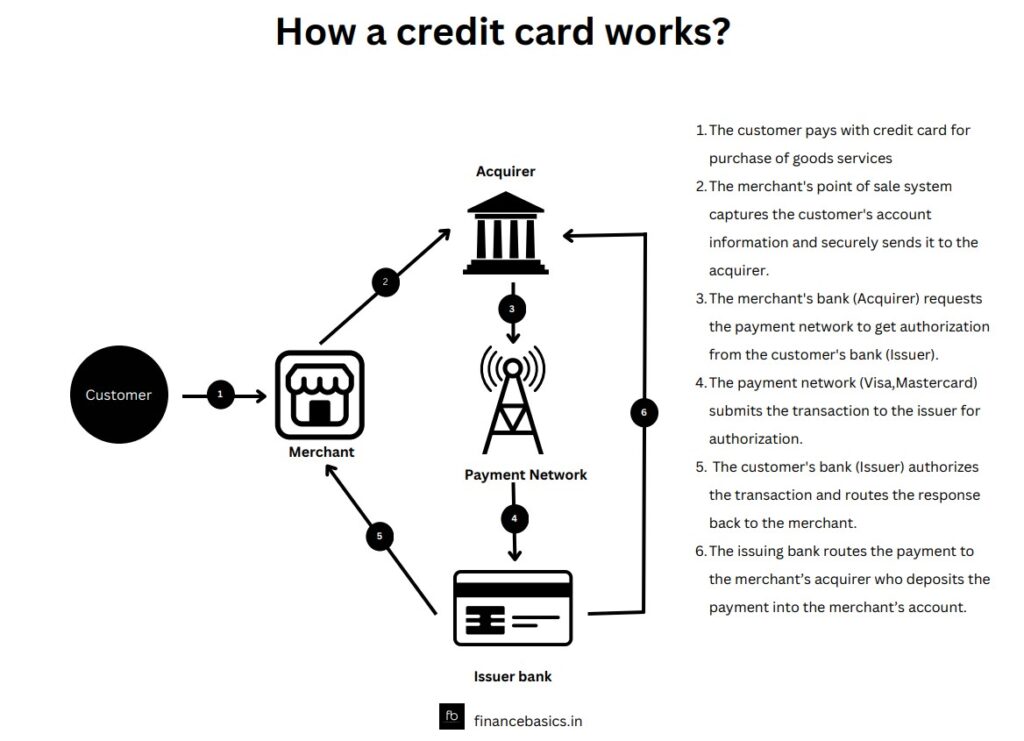
How credit card works?
To understand how a credit card works lets first get to know the three important parties involved in a credit card transaction apart from the cardholder and the merchant.
- An Acquirer – An acquirer is the merchant bank. It is a bank or financial institution licensed by the payment network that helps a merchant fulfill its obligation to accept credit card.
- Issuer – An issuer is the bank or financial institution that provides a credit card to a consumer or business.
- Payment Network – They process payments between the issuing bank and merchants for credit card spends. Visa and MasterCard are two of the largest payment networks in India and worldwide for credit card transactions.
Types of Credit Cards
- Regular Unsecured Credit Cards – These are cards for daily use and a great choice for a ‘first’ credit card. These offer all the convenience and safety of a credit card and combine it with benefits like reward points and fuel surcharge waivers. There are also add on credit cards which one can give to their spouse, adult children and parents.
- Secured Credit Cards – These are issued against fixed deposits. The fixed deposit amount acts as collateral for the credit limit. Secured cards are best-suited for first-time borrowers and those with a poor credit history.
- Co-branded Credit Cards – These are offered by banks in partnership with a brand, such as an airline, hotel chain, or retail store. These credit cards are designed to offer rewards and benefits that are specific to the brand, and often provide cardholders with exclusive discounts, access to special events, and other perks
- Business Credit Cards – These are offered to business owners for work-related expenses. These cards typically come with a high credit limit, longer interest-free credit periods, accelerated cashbacks on business-related spends, etc. These cards help fund and manage business expenditures by tracking expenses and cash flows. They also bring a host of business-related perks like cash advance facility, hotel and travel benefits, and insurance covers.
- Student Credit Cards – These are beginner cards offered to college students with a limited credit history. Students above the age of 18 years can apply for these cards with minimum documentation. While student cards offer perks like Interest-free periods, reward points, and discounts, they also come with a limited credit limit. Student credit cards aid in making college-goers financially responsible and help them build a credit history.
- Premium Credit Cards – Premium cards give higher credit limits, more handsome reward points and more benefits. These provide benefits like free lounge access at airports. These cards normally have higher renewal charges.
- Cashback Credit Cards – These allow one to earn cash back on everyday spends. These cash back are in the form of rewards which one can use to settle the outstanding amount on the credit card. In addition, there are also benefits such as shopping and dining discounts.
- Prepaid Credit Cards – Prepaid credit cards are loaded with funds and customers can make purchases using the funds available on the prepaid card. The best feature of prepaid credit cards is that customers do not incur debts and do not pay huge interests. Purchases can be made until funds are available in the card.
Key Terms
Below are some of the main key terms relating to credit cards which everyone should be aware of.
- Annual Fee – The issuing bank or financial institution charges an annual fee on credit card for the services they provide. On some cards the annual fee is charged from the second year onwards. Some cards are issued free for lifetime use.
- Total Credit Limit – This is the total spending limit or credit line given by the credit card provider. The credit limit varies from person to person and depends on factors like income, credit history, repayment history etc.
- Available Credit Limit – This is the total credit limit – limit used. Suppose your total credit limit is Rs 100,000.You have spent Rs 25,000 using credit card. Here the available credit limit is Rs 75,000 (Rs 100,000- Rs 25,000).
- Utilized Credit Limit – This is the amount of credit used by the cardholder. In the above example, Rs 25,000 has been spent using the credit card. So the utilized credit limit is Rs 25,000.
- Cash Limit – It refers to the maximum amount of cash that a cardholder can withdraw using the credit card. The cash limit varies from bank to bank.
- Total Amount Due – It is the amount due for payment as on the credit card statement date. It consists of one’s opening balance, new purchases, fees, and finance charges if any, minus the last payment or any other due credits.
- Minimum Amount Due – It is the minimum amount that one is required to pay, on or before the due date, to avoid late payment penalties and negative remarks on the credit report. It is recommended to pay the total amount to avoid the rate of interest which is charged on the remaining amount from the date of purchase and on the current month statement as well.
- Billing Cycle – It is the period between the previous statement and the next statement. Suppose the credit card statement is generated on 4th of every month, the billing cycle will be 5th of the month to the 3rd of the next month. Most banks/credit card providers have a 30 days billing cycle.
- Due Date – This is the fixed monthly date when all outstanding payments to the bank, including EMIs, must be paid.
- Interest Rate – Interest charges on a credit card can differ. The interest rate on EMI will be different from interest charged for a cash advance or an over-limit charge.



